Imagine pulling raw gold from the depths of the Earth—it’s exciting, right? But that’s just the start. The gold refining process is where the real magic happens: the final, crucial step that transforms gritty gold ore into gleaming, pure metal ready for the market, jewelry, or investment. While gold mining is all about digging up that ore, gold refining sweeps away impurities to hit the high purity levels everyone demands.

For most modern gold plants, refining begins not from recycled gold, but directly from gold ore—often through a series of leaching, adsorption, desorption, and electrolytic steps. The purpose of gold refining is to achieve consistent purity, high recovery, and sustainable processing with minimal environmental impact.
Use the table of contents below to navigate through the guide:
01How Is Gold Refined? – Step-by-Step Overview
The refining of gold from ore typically follows a systematic process:
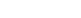
1. Crushing and Grinding
The mined ore is crushed and ground to liberate gold particles. Ball mills and classifiers ensure that the material is reduced correctly to the desired size for the next stage.

2. Leaching and Adsorption
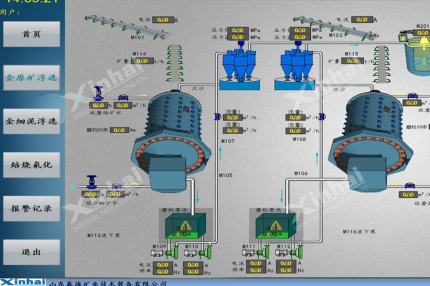
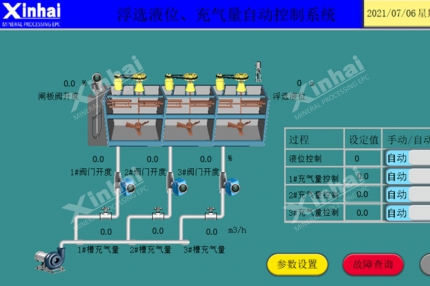
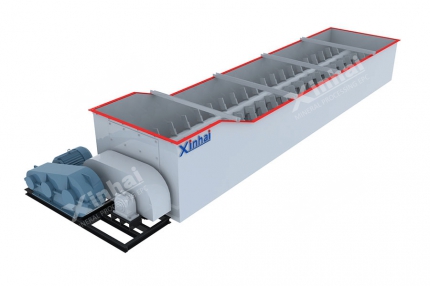
Finely ground ore is subjected to cyanide leaching, dissolving gold into a solution. Modern plants use the Double-impeller Leaching Agitation Tank, which ensures uniform mixing and efficient gold dissolution through enhanced oxygen transfer and slurry circulation.
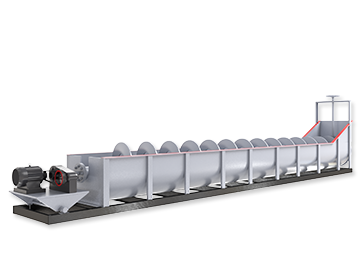
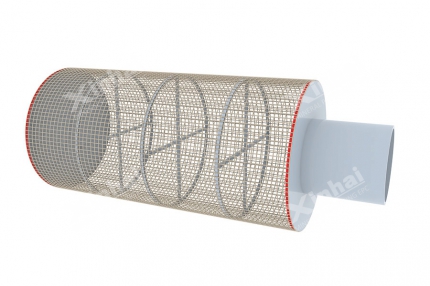
The gold-cyanide solution is then transferred to Carbon Adsorption Columns, where activated carbon captures dissolved gold particles. Between tanks, the Carbon Screen prevents carbon loss and ensures stable adsorption efficiency.

3. Desorption and Electrolysis
Once the carbon is saturated with gold, the metal is stripped using a High-Efficiency, Low-Consumption Desorption Electrolysis System.
This advanced unit integrates heating, stripping, and electrolysis into a single, closed-loop system, enabling rapid gold recovery with minimal reagent consumption.
The Deoxidation Tower ensures a stable electrolysis environment by removing dissolved oxygen. At the same time, an Air Lifter provides a gentle solution for circulation between tanks. Through electrolysis, pure gold deposits onto the cathode plates.

☞Click to unlock the advantages of Xinhai's three-layer desorption electrolysis system.
4. Carbon Regeneration and Recycling
After desorption, the activated carbon is reactivated using a Carbon Regeneration Furnace, restoring its adsorption capacity and reducing operational costs. This closed-loop reuse aligns with the principles of sustainable refining.

5. Concentration and Filtration
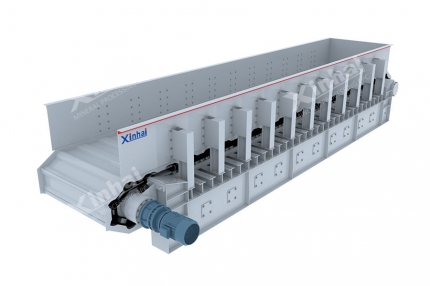
Before final smelting, the gold-bearing solution is often thickened and washed using a Multi-layer Washing Thickener. This equipment removes residual impurities, maximizes recovery, and reduces water usage.

6. Smelting and Final Refining
The gold precipitate is melted in a furnace to remove any remaining base metals. Fluxes such as borax or silica are added to purify the molten metal. The product, known as doré, is then subjected to chemical or electrolytic refining for final purification.

02Smelting vs. Refining: What’s the Difference?
People often confuse smelting and refining, but they’re not the same process. Smelting’s the rough-and-tumble separation from ore; refining’s the finesse work for ultimate purity. Here’s a quick side-by-side:
| Aspect | Smeltin | Refining |
|---|
Purpose | Separate gold from ore | Remove impurities to achieve high purity |
Temperatur | > 1000°C | Moderate, often room temperature |
Main Methods | Furnace melting, flux treatment | Chemical leaching, electrolysis |
Typical Purit | 90–95% | Up to 99.99% |
Output | Doré bullion | Refined gold bar |
Bottom line: Smelting provides a solid foundation, but refining—particularly electrolytic refining of gold—delivers the pristine material that investors and makers crave.
03Electrolytic Refining of Gold
Want gold that’s pure as can be? Enter the electrolytic refining of gold—a go-to method for hitting 99.99% purity, whether in massive plants or lab benches. It’s straightforward yet precise:
The impure gold acts as the anode.
A thin plate of pure gold serves as the cathode.
The electrolyte contains gold chloride (AuCl₃) solution.

Flip the switch: Gold ions migrate, dissolving from the anode and rebuilding pure on the cathode. Junk either floats in the solution or drops as anode slime—a bonus that might hold silver or platinum.
By integrating systems such as the Desorption Electrolysis System and Deoxidation Tower, modern plants achieve faster recovery rates and lower energy consumption.
04Purification of Gold: Achieving the Highest Purity
Purification of gold is the final step, ensuring that standards and checks are in place to achieve flawless results. We talk purity in karats (K) or fineness (parts per thousand)—here’s the breakdown:
| Purity | Description | Application |
|---|
| 99.99% (24K) | Fully refined gold | Investment bullion, electronics |
| 99.5% | Standard refinery output | Jewelry, industrial materials |
| 90–95% | Doré or semi-pure | Intermediate for further refining |
Dial in the heat, current, and chemistry right, and every batch comes out consistently stellar.

05Chemicals Used in Gold Refining
Chemicals are the unsung heroes in gold processing—they dissolve, snag, and purify like pros. The chemicals used in gold refining depend on your approach, but here’s the usual lineup:
| Chemical | Function | Notes / Safety |
|---|
| Sodium Cyanide (NaCN) | Dissolves gold during leaching | Highly toxic; handle with care |
| Aqua Regia (Nitric + Hydrochloric acid) | Dissolves gold and impurities in refining | Produces corrosive fumes |
| Hydrochloric Acid (HCl) | Used in desorption-electrolysis cleaning | Requires ventilation |
| Zinc Powder | Precipitates gold from solution | Flammable; store safely |
| Sodium Metabisulfite (Na₂S₂O₅) | Reduces dissolved gold to solid form | Common in small-scale refining |
Working with these? Stick to gold refining safety precautions like personal protective gear, fume hoods, and proper waste treatment—no shortcuts.
06Gold Refining Safety Precautions
Every stage of the gold refining process, from leaching to electrolysis, involves potential chemical and thermal hazards. Key safety precautions include:
Full PPE: gloves, goggles, respirators
Controlled ventilation and gas scrubbing systems
Safe neutralization of acid residues
Regular maintenance of electrical equipment

The environmental impact of gold refining? It’s a hot topic. Cyanide leaching and acid baths can spew nasty waste, but forward-thinking ops are flipping the script:
Closed-loop water recycling
Waste gas absorption units
Carbon regeneration and recovery systems
Eco-friendly leaching alternatives
Xinhai’s integrated refining systems, for instance, emphasize energy efficiency, low reagent consumption, and closed-loop design, aligning with global sustainability trends.
Explore Xinhai Mining’s Gold Refining Solutions
Seeking efficient and eco-friendly equipment for your gold refining plant? Xinhai Mining offers a full range of technologies—from leaching and adsorption systems to desorption electrolysis and smelting equipment—designed to optimize gold recovery while reducing energy and chemical consumption.
Explore Xinhai Mining’s Gold Refining Solutions to discover how innovation turns gold refining into a cleaner, faster, and more efficient process.


 marketing@ytxinhai.com
marketing@ytxinhai.com  0086 13810327080
0086 13810327080 
































































































 CHAT
CHAT MESSAGE
MESSAGE