Do you think silica sand and quartz sand are the same? Think again! Though they look similar, significant differences exist, making each unique. Let’s break them down to clear your doubts.
This article analyzes their core differences in purification and the process of setting up a silica or quartz sand processing plant. Read on to learn pre-project preparations.
Use the table of contents below to navigate through the guide:
01Quartz Sand Vs. Silica Sand: Differences in Raw Materials, Properties, and Uses
Quartz and silica sand are often used as if they mean the same thing — especially outside of technical circles. But in reality, the two have a few key differences, mainly in purity, source, processing methods, and typical uses.
Here’s a simple breakdown:
Quartz Sand
Quartz sand is made up mostly of the mineral quartz (SiO₂). It can form naturally or be produced by crushing quartz rocks or quartzite.
It’s usually known for its high purity — often above 99.9% SiO₂, and sometimes even at 99.99% or higher. The amount of impurities such as Fe₂O₃, Al₂O₃, CaO, and MgO is extremely low, making quartz sand ideal for high-end industrial uses like electronics and glassmaking.

Silica Sand
Silica sand is a naturally occurring sand that’s mainly made up of silicon dioxide (SiO₂). It technically includes quartz sand, but it’s a broader category.
It can come from the weathering or sedimentation of many silicate minerals. The purity can vary enormously — from high-purity grades like quartz sand to lower-quality sands containing feldspar, mica, clay, or iron minerals.
Simply put, the quality and purity of silica sand depend on what it’s being used for.

Quartz Sand vs Silica Sand: A Detailed Comparison
| Property | Quartz Sand | Silica Sand |
|---|
| Core Definition | Sand particles mainly composed of quartz minerals | Naturally occurring sand mainly composed of silicon dioxide (SiO₂) |
| Key Feature | Dominated by mineral composition (quartz) | Dominated by chemical composition (silicon dioxide) |
| Purity | Generally very high purity (SiO₂ > 99.9%) with low impurities | Purity varies widely — can be high or low, often mixed with other minerals |
| Main Sources | Natural quartz rock, quartz veins (often high-purity deposits) | River, beach, wind-blown, or marine sands (naturally deposited materials) |
| Processing | More complex: crushing, grinding, magnetic separation, flotation, acid leaching, etc. | Relatively simple: mainly washing, cleaning, and sieving (depending on the requirement) |
| Typical Shape | Angular or sharp-edged particles (especially when artificially crushed) | More rounded particles (especially from natural deposits) |
| Main Applications | High-end industries: semiconductors, optics, photovoltaic glass, specialty glass, precision casting, high-purity quartz products | General industries: construction, ordinary glass, foundry, cement, water treatment, sports fields, oil and gas, etc. |
02How to Start a Silica Sand or Quartz Sand Processing Plant?
Starting a quartz sand or silica sand processing plant involves many moving parts — from technical design to legal compliance and business planning. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you understand what’s involved and how to get started.
1. Initial Planning and Feasibility Study
Before investing, conduct a comprehensive preliminary study to determine whether your project is viable. This stage sets the foundation for success.
Key tasks include:
Ore testing and resource estimation – understand the quality and quantity of your raw material.
Market research – identify demand, competitors, and target customers.
Business plan and profitability analysis – calculate startup and operating costs, estimate revenue based on market prices, and project your payback period.

2. Core Processing Stages and Equipment
Processing silica or quartz sand involves several stages to remove impurities and achieve the desired grain size and purity. A typical production line includes the following steps:
Process Flow:
Crushing → Washing → Screening & Classification → Beneficiation (Scrubbing, Washing & Desliming, Magnetic Separation, Flotation, Acid Leaching) → Dewatering & Drying → Packaging
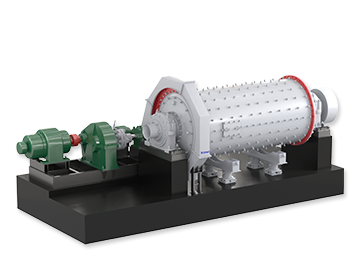
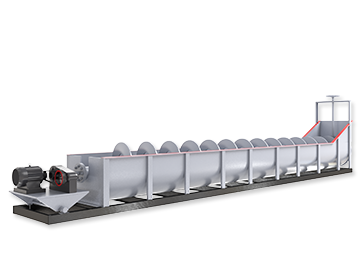
Quartz sand beneficiation equipment mainly includes rod mills, rod flotation machines, hindered settlers, hydrocyclones, high-frequency dewatering screens, lamella thickeners, attrition scrubbers, desliming cones, and slurry pumps.

☞ Click to view more mineral processing equipment
3. Five Common Quartz Sand Processing Methods
Quartz sand beneficiation mainly aims to purify quartz by removing trace impurities and obtaining refined or high-purity sand.
Xinhai’s purification process combines scrubbing, washing, desliming, magnetic separation, flotation, acid leaching, and microbial leaching — ideal for quartz sands containing iron or mica.
(1) Scrubbing
Removes surface iron coatings and clay impurities through mechanical friction. Common methods include rod mill scrubbing and mechanical scrubbing.
(2) Washing & Desliming
A pre-treatment step that removes clay and fine particles before further separation, effectively improving the SiO₂ grade.
(3) Magnetic Separation
Uses high-intensity magnetic separators (over 10,000 Oe) to remove weakly magnetic minerals such as hematite, limonite, and biotite.
(4) Flotation
Targets impurities like feldspar and mica. There are fluorine-based and fluorine-free flotation methods, which are more eco-friendly and efficient.
(5) Acid Leaching
Applies mixed acids to dissolve Fe, Al, Ti, and Cr impurities. By optimizing parameters, this process achieves high purity at a lower cost.
After these treatments, quartz purity can reach over 99%, meeting industrial-grade requirements for glass, ceramics, and electronics applications.
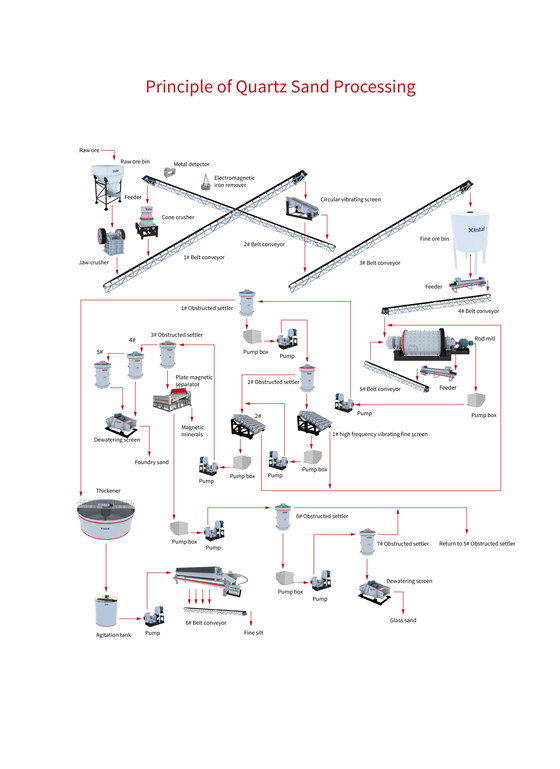
03Choose the Right Quartz Sand Processing Solution for Your Project
① Accurate Laboratory Testing
Xinhai’s advanced laboratories are fully equipped for mineral testing — including crushing, grinding, roasting, drying, spectrometry, atomic absorption, and infrared ore analysis.
Our beneficiation labs can perform tests for gravity separation, magnetic separation, flotation, cyanide leaching, bacterial oxidation, acid leaching, wet separation, heap leaching, and tailings dewatering.
② Innovative Test Design
Each ore sample is unique. Xinhai’s R&D team designs customized test programs based on the specific mineral characteristics of every sample.
For example, we’ve developed over 29 innovative process technologies in gold processing alone, reflecting our commitment to continuous improvement.
③ Representative Sampling for Complex Ore Sources
Many mines source ores from multiple deposits with different characteristics. To ensure representativeness, Xinhai uses a systematic sampling and testing process:
Mine capacity planning and sampling
Preparation of different ore samples
Main sample testing and secondary verification
Final process recommendation and mining design
Construction and production planning
Blending and beneficiation according to the designed capacity plan
This ensures consistent processing performance and reliable beneficiation results even for complex, multi-source ore deposits.
No matter whether it’s silica sand or quartz sand, both are widely used in everyday life and across various industries.
If you’d like to learn more or plan to set up a silica sand or quartz sand processing plant, contact Xinhai China today for customized equipment and factory-direct prices!


 marketing@ytxinhai.com
marketing@ytxinhai.com  0086 13810327080
0086 13810327080 
































































































 CHAT
CHAT MESSAGE
MESSAGE