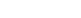
Copper-molybdenum ore usually contains copper, molybdenum and other associated minerals. Its beneficiation process needs to comprehensively consider the mineral composition, particle size distribution and mineral characteristics of the ore. The entire copper-molybdenum ore beneficiation process includes multiple links such as crushing, grinding, and flotation. Each link has an important impact on the final concentrate quality and recovery rate. Understanding and mastering the beneficiation process of copper-molybdenum ore will not only help improve the processing efficiency of ore, but also maximize the recovery rate of copper and molybdenum and realize the rational use of resources. The following will introduce you to the beneficiation process of copper-molybdenum ore to help you become more familiar with the processing technology of copper-molybdenum ore.
Use the table of contents below to navigate through the guide:
01Copper-molybdenum ore coarse crushing and grinding
The copper-molybdenum ore is first coarsely crushed and then transported to the ore storage pile. The ore is initially ground in a semi-autogenous ball mill, and the discharge is screened by a vibrating screen. The screened product is sent to a crusher for re-crushing, and the crushed product re-enters the semi-autogenous ball mill. The undersize product is separated by a hydrocyclone, and the underflow enters the ball mill for further grinding. The discharge returns to the hydrocyclone for classification.

02Copper-molybdenum ore roughing and regrinding
The overflow of the hydrocyclone enters the flotation machine, and the copper-molybdenum roughing is carried out using butyl xanthate and frother. The tailings after roughing are sent to the tailings pond, and the flotation foam product enters the regrinding stage. The regrinded slurry is processed with the hydrocyclone through a closed-circuit process, and the overflow product enters the flotation column for selection.
03Copper-molybdenum separation
The foam product of the flotation column is dehydrated and dehydrated by the thickener, and then enters the sealed flotation machine for copper-molybdenum separation. Sodium hydrosulfide is used as a depressant. During the separation process, the sealed flotation machine effectively prevents the smell of hydrogen sulfide from emitting, improving the working environment of the workshop. This design is innovative in terms of humanized operation.

04Treatment of copper concentrate and molybdenum concentrate
The tailings after copper and molybdenum separation are copper concentrates, which are sent to copper smelters for smelting after being processed by concentrators and filter presses. The flotation column foam product is further refined to obtain molybdenum concentrate, which is concentrated by a thickener and then filtered by a filter press, and finally dried and packaged for shipment.
05Optimization of copper-molybdenum ore flotation process equipment
In recent years, molybdenum plants have widely used KYF-type, XCF-type and other slurry-suction aerated mechanical agitation flotation machines, as well as BF-type and SF-type self-aspirated mechanical agitation flotation machines. However, with the increase in ore fineness requirements, especially when the ore fineness after regrinding reaches 48μm or even 30μm, traditional flotation equipment has certain limitations in processing high-fineness minerals.

Compared with traditional flotation machines, flotation columns have obvious advantages in the selection process, such as stronger controllability of foam layer thickness, bubble size, and quantity, and simplified flotation process. In addition, the flotation column has a better separation environment when processing fine or micro-fine molybdenum ore, and is easy to realize automatic control, so it is very suitable for the concentration of molybdenum ore. This technology has been widely used in many copper-molybdenum concentrators around the world.
06Copper-molybdenum ore coarse grinding, coarse selection, regrinding and reselection process
Due to the natural hydrophobicity of molybdenite, hydrocarbon oils (such as steam oil, kerosene, diesel, etc.) have been used as collectors for a long time, and the mineral processing process is also constantly optimized. Scientists use the process of rough grinding, coarse selection, grinding and re-selection to float the coarse-grained molybdenite conjoints first, and then realize the dissociation of molybdenite and gangue minerals through re-grinding, and finally obtain single molybdenite. This process improves oil dispersion by using steam oil or kerosene emulsifiers to enhance molybdenite flotation efficiency.

The copper-molybdenum ore beneficiation process is a complex and delicate process, involving multiple links from ore coarse crushing and grinding to flotation, separation and final concentrate processing. By rationally optimizing the equipment and processes in each link, we can not only improve the efficiency of ore processing, but also significantly increase the recovery rate of copper and molybdenum, maximizing the economic utilization of resources. With the continuous advancement and optimization of mineral processing technology, the processing technology of copper-molybdenum ore will become more refined and automated, promoting the development of mining production in a more efficient and environmentally friendly direction.


 marketing@ytxinhai.com
marketing@ytxinhai.com  0086 13810327080
0086 13810327080 
































































































 CHAT
CHAT MESSAGE
MESSAGE