As the global electric vehicle and energy storage markets experience explosive growth, the strategic importance of hard rock lithium resources—primarily spodumene—has become increasingly prominent. Compared to brine extraction, the flotation process remains the most mature and cost-effective pre-concentration method for hard rock ores.
This article integrates frontline engineering practices with authoritative technical theory to provide a practical guide for engineers and decision-makers in lithium flotation. We go beyond analyzing core process principles to deeply explore how optimized reagent design, equipment strategies, and process flow enhancements can transform low-grade ores into high-value concentrates.
Use the table of contents below to navigate through the guide:
01Core Process Explained: The Transformation from Ore to Lithium Concentrate
Lithium flotation is essentially a precise physical-chemical separation chain. Understanding the critical control points at each stage is essential:
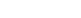
1. Crushing and Grinding (Preparation Stage)
This is the foundation that determines flotation success. Run-of-mine ore must be coarse-crushed by jaw and cone crushers before entering ball mills and classification systems.
Key Objective: Monomer Liberation. Ensuring spodumene is fully freed from gangue minerals like quartz and feldspar is paramount.
Core Challenge: Particle Size Control. Excessively coarse particles lead to inadequate liberation and lower recovery rates; overgrinding generates excessive slimes (fine particles), increasing reagent consumption and deteriorating the flotation environment. Balancing the grinding circuit with classification efficiency is the design focus here.
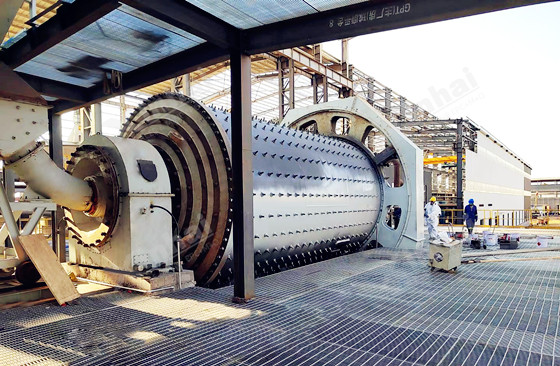
2. Reagent Addition and Pulp Conditioning (Chemical Intervention)
Before entering flotation cells, the pulp must be adjusted to optimal concentration and environmental conditions. A “reagent scheme” customized to ore characteristics is the core technology:
Modifiers (e.g., NaOH, Na₂CO₃): Adjust pulp pH and mineral surface electrical properties to create conditions for spodumene flotation.
Collectors (e.g., Fatty Acids): Selectively increase the hydrophobicity of lithium minerals, making them easily attachable to air bubbles.
Depressants (e.g., Starch, Dextrin): Precisely suppress the flotation of unwanted gangue minerals like quartz and feldspar.
Frothers (e.g., Pine Oil): Stabilize bubble structure to improve carrying efficiency.

3. Flotation Separation (Physical Separation)
The conditioned pulp enters flotation cells and is aerated. Hydrophobic spodumene particles attach to rising bubbles to form a froth layer (concentrate), while hydrophilic gangue minerals remain in the pulp as tailings. The concentrate is subsequently thickened and dewatered to form the final high-grade lithium concentrate product.

02Beyond Theory: Strategies for Driving Industrial-Grade Efficiency
In practice, improving flotation efficiency is far more complex than following a theoretical flowsheet. High-efficiency operations require comprehensive, multi-dimensional optimization:
1. Refined Particle Size and Pulp Management
Grinding circuits must find the equilibrium between “liberation efficiency” and “optimal flotation size distribution,” minimizing interference from both oversize particles and ultra-fine slimes.
2. Intelligent Reagent Control
Moving beyond empirical, fixed-point addition. Modern processes combine online pH and Zeta potential monitoring to dynamically fine-tune the ratio of collectors and depressants, maintaining stable flotation performance.

3. Automated Process Control (PLC/DCS)
Integrating control systems with flotation kinetic models allows for automatic adjustment of aeration rates, pulp levels, and reagent dosages. This is a critical step in moving process stability from “manual intervention” to “systematic control.”
4. Multi-Stage Flotation and Regrinding Strategies
For refractory ores with fine dissemination or complex intergrowth, adopting a multi-stage “rougher-cleaner-scavenger” combination, paired with intermediate regrinding, is a proven path to improving overall recovery and concentrate grade.
03Integrated Design: Building a High-Performance Lithium Processing Plant
Designing an efficient lithium beneficiation plant is not merely about purchasing flotation machines; it is about constructing a coordinated system that integrates mineralogy, metallurgy, engineering design, and lifecycle costs.
From Lab to Industry: Crossing the Gap
Metallurgical testing defines theoretical recovery potential, but industrial stability depends on the implementation of engineering details:
Optimized crushing and grinding circuit configurations.
Flexible rougher-cleaner-scavenger layouts.
Controlled regrind stages where necessary.
Efficient thickening, filtration, and tailings handling systems.
Addressing Ore Variability: Pegmatite deposits often face fluctuations in grade, varying mica content, and iron contamination. Modular design and flexible circuit configurations are key to de-risking operations.

Equipment Selection: Performance Over Parameters
When evaluating suppliers, decision-makers should look beyond equipment size and power ratings to focus on long-term performance indicators:
Hydrodynamic design and dispersion efficiency of flotation cells.
Wear resistance under abrasive ore conditions.
Mechanical vs. Column: Mechanical cells remain mainstream, but column flotation is increasingly used in cleaning stages to boost grade. Hybrid systems often handle complex ores better.
Supplier Capability: Reliable suppliers provide not just hardware, but full lifecycle services including test validation, commissioning support, and process optimization.

04Future Trends: Engineering Integration and Digital Empowerment
The success of modern lithium projects increasingly depends on system integration capabilities rather than the performance of individual equipment pieces.
1. EPC and Full-Process Engineering CapabilityIn the competitive lithium market, EPC (Engineering, Procurement, Construction) providers with comprehensive beneficiation experience possess distinct advantages. Rather than offering isolated machines, they integrate crushing, grinding, flotation, and dewatering into a cohesive operating system through detailed mineralogical analysis, customized reagent schemes, and pilot-scale verification.
With over 30 years of mineral processing expertise and 2100+ overseas projects delivered, Xinhai Mining exemplifies this full-process EPC+M+O capability, combining in-house equipment manufacturing with systematic testwork-driven design. This system-level approach directly contributes to achieving optimized flotation efficiency at scale.
2. Digitalization and Long-Term Operational Optimization
The next generation of lithium plants is deeply integrating digital technologies to enhance operational certainty:
Real-time process monitoring and on-stream particle size/grade analyzers.
Automated dosing systems and energy consumption tracking.
Predictive maintenance models.
These digital tools not only stabilize recovery rates and reduce reagent consumption but are also critical levers for improving a project’s ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) performance. For emerging lithium projects, partnering with companies capable of integrated design and digital vision is the optimal path to reducing technical and financial risks.


 marketing@ytxinhai.com
marketing@ytxinhai.com  0086 13810327080
0086 13810327080 
































































































 CHAT
CHAT MESSAGE
MESSAGE